

Inter-trochanteric, which are between the greater trochanter and the lesser trochanter.Extra-capsular – outside the capsule, subdivided into:.Intra-capsular – from the subcapital region of the femoral head to basocervical region of the femoral neck, immediately proximal to the trochanters.The neck of femur can be considered to have two distinct areas, which are described relative to the joint capsule: 1).įigure 1 – The bony landmarks of the anterior proximal femur Neck of femur (NOF) fractures can occur anywhere from the subcapital region of the femoral head to 5cm distal to the lesser trochanter (Fig.
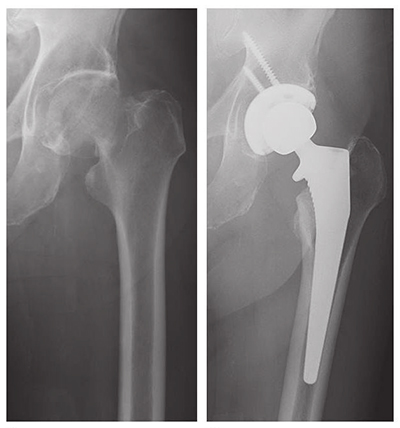
In this article, we will look at the classification, anatomy, clinical and radiological features, and management of neck of femur fractures. Neck of femur fractures are typically caused either by l ow energy injuries (the most common type), such as a fall in frail older patient, or h igh energy injuries, such as a road traffic collision or fall from height and are often associated with other significant injuries. The mortality of a femoral neck fracture up to 30% at one year consequently, these fractures require specialist care and, indeed, most orthopaedic units now have dedicated orthogeriatricians who specialise in the care of this vulnerable patient group. Over 65,000 hip fractures each year are recorded in the UK and they are becoming increasingly frequent due to an aging population. A fractured neck of femur (NOF) is a very common orthopaedic presentation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
